As global water scarcity grows, homeowners are looking for innovative and eco-friendly plumbing solutions to conserve water and reduce waste. One of the most effective and sustainable systems gaining popularity is the greywater recycling system. This technology allows households to reuse wastewater safely, helping conserve fresh water and reduce utility bills—all while minimizing environmental impact.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore what greywater systems are, how they work, their benefits, and how to integrate them into your home’s plumbing system for maximum sustainability.
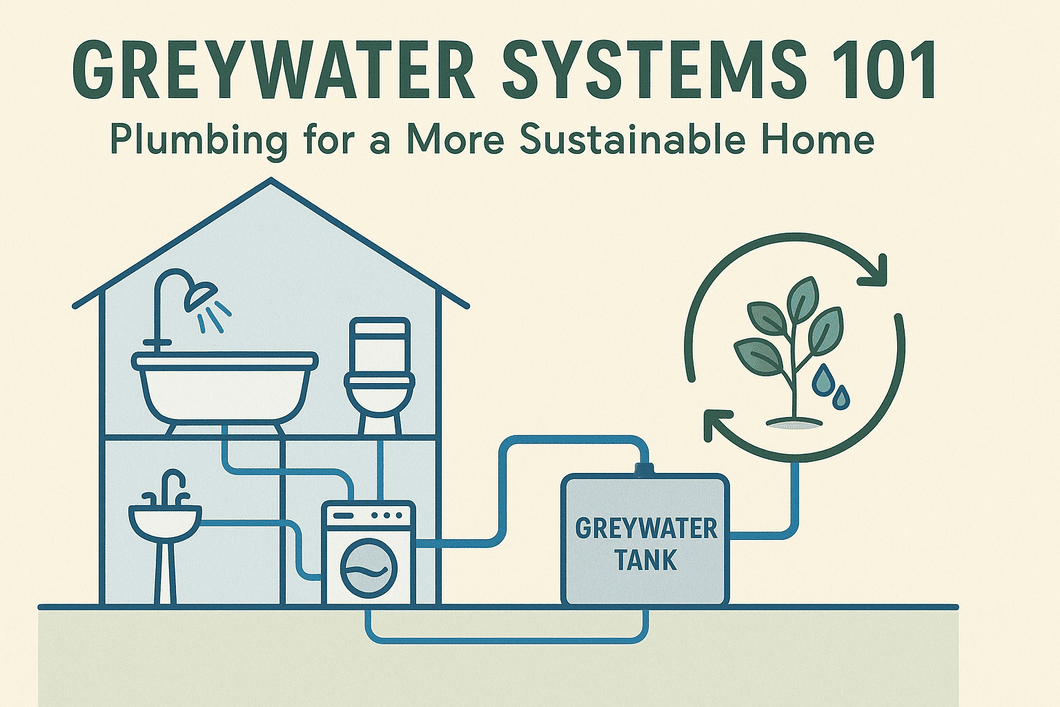
What Is a Greywater System?
Greywater refers to gently used household wastewater that comes from sinks, showers, bathtubs, and washing machines. It does not include water from toilets, which is classified as blackwater due to its higher contamination level.
Greywater systems are designed to collect, filter, and reuse this lightly contaminated water for non-potable purposes such as:
- Garden and lawn irrigation
- Toilet flushing
- Laundry prewash cycles
- Outdoor cleaning and car washing
By diverting greywater for these uses, households can reduce freshwater consumption by up to 40%, depending on the system and usage patterns.
How Greywater Systems Work
A typical greywater system involves several components that work together seamlessly to capture, treat, and distribute the water. Here’s how it works step by step:
- Collection Stage:
Greywater is collected from approved plumbing fixtures (such as showers, bathroom sinks, and laundry machines). - Filtration Stage:
The collected water passes through filters or settling tanks that remove hair, lint, and debris. - Treatment Stage:
Depending on the system’s design, biological or chemical processes may be used to treat the water—removing bacteria and balancing pH levels. - Storage Stage:
The treated greywater is stored in a dedicated holding tank equipped with safety valves and overflow protection. - Distribution Stage:
The system then pumps or gravity-feeds the treated water to irrigation systems, toilet cisterns, or other designated uses.
The entire process ensures the water is safe, odor-free, and environmentally compliant.
Types of Greywater Systems
There are different types of greywater systems designed for varying budgets, property sizes, and usage needs. The most common types include:
1. Direct Diversion Systems
These are basic and cost-effective systems that collect greywater from specific fixtures and redirect it immediately for irrigation or outdoor use.
- Pros: Affordable and simple installation
- Cons: Limited treatment; suitable only for subsurface irrigation
2. Branched Drain Systems
In this setup, gravity flow is used to distribute greywater through a network of branching pipes.
- Pros: Low maintenance, energy-efficient
- Cons: Requires proper slope and careful planning
3. Filtered and Pumped Systems
These include mechanical filters and electric pumps that allow water to be reused indoors for toilet flushing or laundry.
- Pros: Suitable for urban homes
- Cons: Higher installation and maintenance costs
4. Advanced Treatment Systems
These high-end systems use UV disinfection, biofilters, and membrane filtration to treat greywater to a high standard, making it ideal for commercial or large residential applications.
- Pros: Produces high-quality water
- Cons: Expensive and requires professional maintenance
Benefits of Installing a Greywater System
Integrating a greywater system into your home is a powerful step toward sustainability. Let’s explore the key benefits:
1. Water Conservation
With freshwater resources under pressure, recycling greywater can reduce total water use by thousands of gallons annually.
2. Cost Savings
Households can experience a significant reduction in water bills, especially in regions with high utility rates or water restrictions.
3. Eco-Friendly Landscaping
Greywater provides nutrient-rich irrigation, promoting healthier plant growth and soil moisture retention without added chemical fertilizers.
4. Reduced Strain on Municipal Systems
By reducing wastewater discharge, greywater systems help lessen the load on local sewage infrastructure and treatment plants.
5. Sustainability and Resilience
In drought-prone areas, a greywater system offers reliable water reuse options, making homes more resilient to water shortages.
Design and Installation Considerations
Before installing a greywater system, it’s crucial to evaluate several design and regulatory factors.
1. Local Regulations
Check municipal and state plumbing codes to ensure your system complies with safety and environmental standards.
2. System Size and Type
Select the right system based on household size, water usage habits, and available space.
3. Plumbing Integration
Work with licensed plumbers to retrofit existing plumbing lines for greywater collection while maintaining separation from blackwater.
4. Maintenance Needs
Regular cleaning of filters, pumps, and tanks is vital to ensure efficient and hygienic operation.
5. Cost and ROI
Installation costs can range from $1,000 for simple systems to $10,000+ for advanced setups, depending on complexity. However, long-term water savings often offset the initial investment within a few years.
Greywater vs. Rainwater Harvesting
While both systems promote water conservation, they serve distinct purposes:
| Aspect | Greywater System | Rainwater Harvesting |
| Source | Used indoor water (sinks, showers) | Rainfall collected from rooftops |
| Treatment | Filtration and disinfection required | Minimal filtration |
| Usage | Toilets, irrigation, laundry | Irrigation, car wash, potable (with treatment) |
| Complexity | Moderate to high | Low to moderate |
Combining both systems offers the ultimate sustainable water management solution for eco-conscious homeowners.
Maintenance Best Practices
To keep your greywater system running efficiently, follow these essential maintenance tips:
- Clean filters and screens monthly to prevent clogging.
- Use biodegradable and low-sodium detergents to avoid soil contamination.
- Inspect tanks and pipes for leaks or blockages every few months.
- Ensure aeration and disinfection units are functioning correctly.
- Schedule annual professional inspections for performance optimization.
By maintaining your system regularly, you’ll ensure long-term efficiency, hygiene, and compliance with environmental standards.
Why Greywater Systems Are the Future of Home Plumbing
The demand for sustainable living is reshaping how modern homes are built and managed. Greywater recycling systems are no longer niche innovations—they’re becoming essential features for environmentally responsible households.
From reducing water bills and supporting green landscapes to promoting long-term sustainability, these systems reflect a forward-thinking approach to water conservation. With growing environmental awareness and government incentives, now is the perfect time to invest in greywater technology.
By embracing eco-smart plumbing, we can collectively take a meaningful step toward a greener, more water-efficient future.