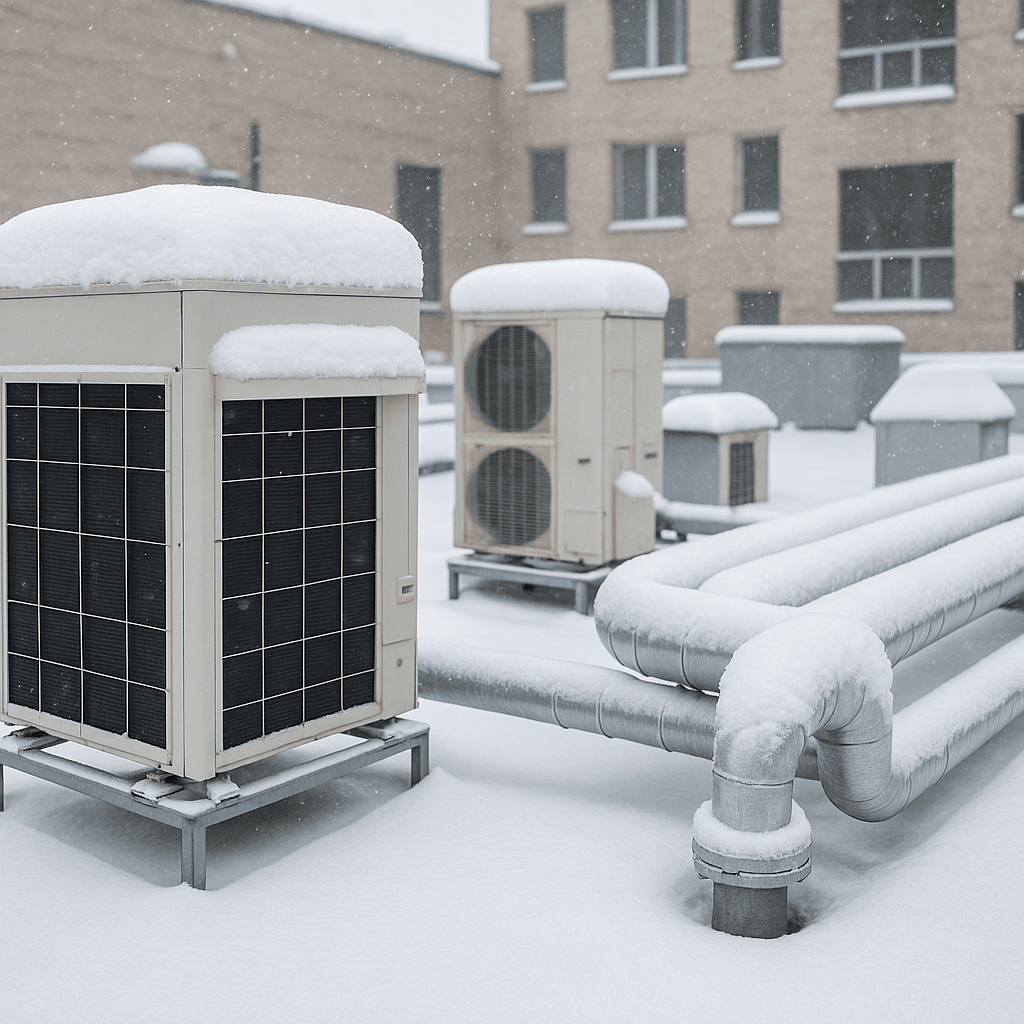
As temperatures drop and frost begins to form, facility managers must take a proactive approach to ensure their buildings remain efficient, comfortable, and safe throughout the winter months. Preparing your mechanical systems for winter is not just about comfort—it’s about protecting assets, maintaining productivity, and avoiding costly downtime.
Why Winter Preparation Matters for Mechanical Systems
When cold weather hits, mechanical systems such as heating, ventilation, and plumbing are put under immense stress. Without proper preparation, these systems can fail when you need them most—leading to frozen pipes, heating inefficiencies, and energy losses that can skyrocket operational costs.
By implementing a comprehensive winter readiness plan, facility managers can avoid breakdowns, maintain indoor air quality, and extend the lifespan of critical assets.
1. HVAC Systems: Your First Line of Defense Against the Cold
Your HVAC system is the heart of your building’s winter comfort. A properly maintained system ensures consistent heat distribution, better air quality, and lower energy bills.
a. Conduct Preventive Maintenance
Before the first snow falls, ensure all heating components are serviced and inspected. Check for:
- Dirty filters and clogged coils
- Malfunctioning thermostats
- Worn-out belts or motors
- Leaks in ductwork or boilers
A professional inspection and tune-up will help ensure maximum heating efficiency and reduce the likelihood of unexpected breakdowns.
b. Calibrate Thermostats and Sensors
Temperature sensors and thermostats must be accurate and responsive. Miscalibration can cause energy waste and uneven heating. Use programmable thermostats to optimize heating schedules and avoid overheating unoccupied spaces.
c. Check Airflow and Insulation
Cold air infiltration can disrupt balanced airflow. Inspect duct insulation and seal leaks around windows, doors, and vents to maintain consistent indoor temperatures and reduce strain on your HVAC system.
2. Boiler and Chiller Systems: Avoiding Mid-Winter Failures
For facilities using boiler or chiller systems, winter can be particularly demanding. Boilers must handle the heating load, while chillers may need to stay operational for process cooling.
a. Boiler System Inspection
Perform a detailed boiler check, including:
- Testing pressure relief valves
- Inspecting burners and heat exchangers
- Cleaning out scale buildup
- Checking for leaks or corrosion
Proper boiler maintenance not only prevents shutdowns but also improves fuel efficiency and reduces emissions.
b. Winterizing Chillers
Even though chillers see less use in winter, they still need protection. Drain systems that are idle during the cold months and add antifreeze solutions where necessary. Neglecting this can result in cracked coils and costly repairs when spring returns.
3. Plumbing and Piping: Preventing Freezes and Bursts
Frozen pipes are one of the most common—and costly—issues in cold weather. When water freezes, it expands, creating immense pressure that can rupture pipes and flood your facility.
a. Insulate Exposed Pipes
All exposed or exterior-facing pipes should be properly insulated using foam sleeves or heat tape. Pay special attention to:
- Crawl spaces
- Mechanical rooms near exterior walls
- Roof drains and outdoor hose bibs
b. Maintain Consistent Temperatures
Keep temperatures above 55°F (13°C) in unoccupied areas. Even a small drop can lead to a freeze event in under-insulated spaces.
c. Test Emergency Shutoff Valves
Make sure all isolation valves and shutoff systems function properly in case of a burst or leak. A quick shutoff can save thousands in damage and repair costs.
4. Ventilation Systems: Balancing Fresh Air and Heat Retention
While heating is critical, proper ventilation must not be neglected. Poor airflow can lead to condensation, mold growth, and indoor air quality issues.
a. Inspect Air Intakes and Exhausts
Clear all vents of debris, snow, or ice buildup. Blocked vents can cause dangerous backdrafting or limit the efficiency of air exchange systems.
b. Optimize Air Balancing
Adjust dampers to maintain positive pressure in warm zones and prevent cold air infiltration. Balancing airflow ensures consistent comfort and energy efficiency.
c. Clean Filters and Ducts
Dirty filters restrict airflow and force systems to work harder. Replace filters and clean ducts regularly to maintain indoor air quality during months when fresh air exchange is minimal.
5. Building Automation Systems: Smarter Control During the Cold
Modern facilities rely heavily on Building Automation Systems (BAS) to regulate comfort and performance. Winter is the ideal time to fine-tune control settings and maximize efficiency.
a. Review Schedules and Setpoints
Optimize heating schedules based on occupancy patterns. Lowering the temperature in unoccupied areas during nights or weekends can yield significant energy savings.
b. Monitor Energy Consumption
Leverage BAS analytics to track energy use trends and identify anomalies. If a heating zone is using more energy than expected, it may signal leaks, insulation gaps, or malfunctioning components.
c. Integrate Predictive Maintenance Alerts
Use predictive monitoring to catch issues before they escalate. Real-time data helps maintenance teams anticipate failures and plan repairs during off-peak hours.
6. Electrical Systems: Power Reliability in Extreme Conditions
Cold weather often brings power surges, outages, and voltage fluctuations. Reliable electrical systems keep your facility operational and safe.
a. Inspect Backup Generators
Ensure generators are tested, fueled, and load-ready. Verify automatic transfer switches function properly, and inspect battery health.
b. Protect Outdoor Equipment
Snow, ice, and condensation can cause electrical short circuits. Protect outdoor panels and seal conduit entries to prevent moisture intrusion.
c. Perform Load Testing
Balance power loads across circuits and conduct a winter stress test to ensure systems can handle peak electrical demands.
7. Roof and Drainage Systems: Defending Against Ice and Water Damage
Mechanical maintenance also extends beyond indoor systems. The roof and drainage systems play a critical role in protecting equipment from leaks and water intrusion.
a. Clean Gutters and Downspouts
Remove leaves, debris, and standing water. Blockages can lead to ice dams that force water under roofing membranes and into interior walls.
b. Inspect Rooftop Equipment
Check that HVAC units and vents are secure and level. Accumulated snow can strain support structures and create uneven heating or airflow patterns.
8. Schedule a Comprehensive Winter Readiness Audit
Every facility has unique demands. The best way to ensure complete readiness is to schedule a professional winterization audit. An experienced mechanical contractor will:
- Assess heating and ventilation performance
- Inspect insulation and energy efficiency
- Identify at-risk systems and components
- Provide a customized maintenance checklist
A winter audit helps create a roadmap for reliable operations, minimizing surprises during the coldest months.
Final Thoughts: Prepare Now, Save Later
Preparing your mechanical systems for winter is an investment that pays off in reliability, safety, and reduced energy consumption. At Korycki Mechanical Inc., we help facilities stay ahead of the cold season with preventive maintenance, energy optimization, and round-the-clock support.
Don’t wait for a breakdown—act now to safeguard your facility’s comfort and efficiency before winter arrives.